MVP development
Product strategy
Security practices
You Built an MVP. Now What? A Guide to Post-MVP Development and Scaling Strategy
Nadiia Sidenko
2025-04-14
Launching a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a milestone — but it’s only the beginning. While many startups celebrate an MVP as a successful launch, the reality is that the hardest work starts after it: post-MVP development, managing technical debt, scaling infrastructure, achieving product-market fit, and ensuring long-term security. This phase determines whether your product becomes sustainable — or collapses under its own growth.

Post-MVP Development: How to Scale Without Breaking the Product
Scaling an MVP too early: why it backfires
After an MVP shows promise, founders often feel the pressure to grow quickly. But rushing into development without stabilizing the core structure leads to avoidable setbacks.
As we discuss in our SaaS MVP strategy article, common growth obstacles stem from MVPs being built quickly, often on shaky architectural foundations.
Post-MVP scaling challenges startups must avoid
- Unoptimized code and skipped refactoring
- Weak infrastructure not ready for high traffic
- Lack of modularity and separation of concerns
- No performance monitoring or release control
- Conflicting priorities across fast-growing teams
Technical debt after MVP: when it becomes critical
MVPs accumulate shortcuts. If not cleaned up, these technical compromises:
- slow down future development
- increase the risk of failure during releases
- drain resources on bug-fixing instead of innovation
Security Risks in Early-Stage Products: What to Fix First
MVP security vulnerabilities explained
Speed-focused MVPs typically bypass rigorous testing and security protocols. That may be acceptable during prototyping, but these risks must be addressed before scaling.
In our guide to mobile app security, we emphasize that MVPs are often exposed through poor authentication, insecure APIs, and lack of encryption — all of which align with the most common threats listed by the OWASP Top Ten, a global standard for web application security risks.
- poor authentication mechanisms
- unencrypted data storage
- unsecured API endpoints
- lack of regulatory compliance planning
Key security risks in MVP software to address first
MVP authentication risks and data exposure issues
Simple login flows may skip validation or session control, leading to vulnerabilities.
Compliance issues in MVPs: GDPR, HIPAA, and more
If your product collects user data, you must align with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA — even if you’re still testing.
Product-Market Fit After MVP: What It Actually Looks Like
What product-market fit really means
Releasing an MVP and getting a few users is not the same as proving market demand. As outlined in our product evolution guide, product-market fit occurs when:
- users return regularly
- the product solves a real, repeatable problem
- usage increases without excessive marketing
- churn rates are low, and retention is measurable
How to move from MVP testing to true validation
Use structured iteration cycles
Product-market fit requires continuous testing and refinement. Base each update on real usage data, not assumptions.
Collect feedback systematically
Feedback isn’t just about opinions — it’s about measurable patterns in behavior and qualitative user signals.
Post-MVP Maintenance and Support: The Cost of Neglect
Why post-MVP product support is crucial for growth
Many startups focus only on building — not maintaining. But once users rely on your product, even a small outage can lead to churn or reputational damage.
In our DevOps implementation guide, we emphasize the importance of post-MVP stability.
What ongoing support includes
- Version control and rollback systems
- Continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD)
- Application performance monitoring
- Bug tracking and release management
- Documentation and technical onboarding processes
Key takeaway:
The post-MVP phase isn’t just about adding features — it’s about laying the groundwork for growth.
Scalable MVP Architecture: Prepare for Real Growth
When to refactor your MVP architecture for scale
In our architecture transformation article, we show how startups that delay infrastructure work often face rebuilds just when their product gains traction.
Key principles for scalable software
- Modular structure and API-first approach
Break your application into self-contained modules. Use clear interfaces (APIs) between components to avoid tight coupling.
- Future-proof with cloud-native tools
Consider using:
- Containerized environments (e.g., Docker)
- Microservices instead of monoliths
- Horizontal scaling with Kubernetes
- Infrastructure-as-code (e.g., Terraform)
Technologies like Kubernetes and Terraform offer powerful tools for automating deployment, scaling, and infrastructure management — making them ideal for post-MVP scalability.
This setup supports easier testing, isolated deployments, and long-term flexibility.
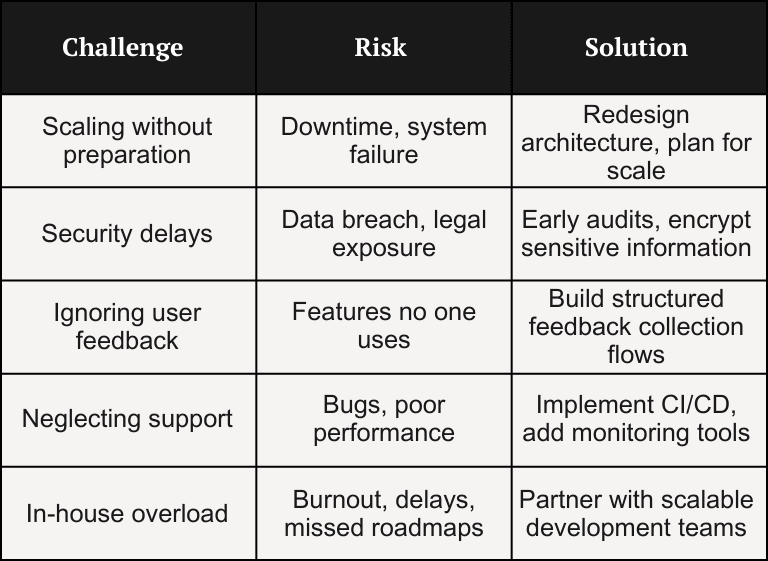
Table: Post-MVP Pitfalls and How to Prevent Them
Partnering After MVP: When Expert Help Becomes Essential
Scaling MVP in-house: challenges internal teams face
Building an MVP in-house works well for validation. But scaling brings new technical demands — DevOps, QA, infrastructure, compliance — that many teams aren’t equipped to handle alone.
As shown in our partnering guide, working with an experienced partner gives you:
- faster development cycles
- access to cross-functional specialists
- predictable costs and clearer planning
- reduced time-to-market through proven frameworks
Conclusion
Post-MVP Is Where Products Are Truly Built
Your MVP is not your product — it's your test. Real success comes from what you do next. If you want to scale with confidence, you need to build not only fast, but right.
That means securing your codebase, scaling your architecture, validating with real users, and maintaining your product as if it were already serving thousands.
The companies that succeed beyond MVP are the ones that treat this next stage seriously — with structure, partners, and strategic decisions.
FAQ: Common Post-MVP Development Questions
Q: When should I start scaling my MVP?
Start when you consistently see user retention and infrastructure strain — not just early interest.
Q: How do I manage technical debt after MVP?
Prioritize cleanup before expanding features. Build sprints focused solely on code refactoring.
Q: What security risks should I address first?
Begin with data storage, authentication, and access control. Then review compliance risks by region.
Q: Is it better to hire in-house or outsource post-MVP development?
For early-stage growth, strategic outsourcing helps you move faster while controlling costs — especially when internal hiring is slow or fragmented.